Treatment Of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus consists of alleviating symptoms by adapting to the clinical situation of each affected person, for which there are many effective pharmacological groups .
Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus is symptomatic. This is why there is no definitive etiological treatment to cure this disease.
There are many treatments that focus on alleviating symptoms. But a general direction of treatment cannot be established. Indeed, each clinical situation of each patient is different.
In each case, it will be necessary to find a consensus and assess the benefits and risks.
Treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus
The most commonly used drugs for the treatment of lupus are:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Glucocorticoids
- Antimalarials
- Immunosuppressants
- Biological therapies
NSAIDs
NSAIDs, such as ibuprofen or paracetamol, are drugs suitable for the symptomatic treatment of musculoskeletal manifestations of illness, fever and seritis.
They are recommended for limited periods in cases where the risk of complications is low.

When these drugs are administered, it is necessary to assess the side effects of digestive, kidney and cardiovascular diseases that may occur, and to avoid using them in kidney disease.
Glucocorticoids
This group of drugs has been the mainstay of treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus due to its anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive ability.
It is the most important and effective treatment against the acute phases of the disease. They thus allow a reduction in mortality.
A disadvantage of glucocorticoids is their long-term consumption, as they exhibit high toxicity which can lead to certain undesirable effects, among other pathologies:
- Osteoporosis: disease associated with the predisposition of bones to their rupture
- Cushing’s syndrome
- Diabetes mellitus
- Increased risk of infections
- Glaucoma: a disease defined by an increase in the pressure of the eyeball. It manifests as progressive deterioration of the retina and loss of vision.
These side effects therefore limit its use: a dose of ≤5 mg / day of prednisone (or equivalent) is recommended.
Despite its high toxicity, all complications can be successfully treated with corticosteroids.
Antimalarials
This group includes chloroquine, in particular hydroxychloroquine. These are drugs prescribed for most patients with SLE and the only drugs with the specific indication for SLE until approval of belimumab, a biologic drug that we will discuss later in this article.
These drugs are mainly used to fight the following conditions:
- Arthritis: inflammation of the joints
- Tired
- Certain skin lesions
- Pericarditis
- General symptoms
Antimalarials are generally well tolerated. However, they are possibly toxic to the retina. For this reason, it is recommended to carry out periodic ophthalmological examinations.
They can be consumed during the gestation period. Indeed, they help to regulate the levels of cholesterol and have an anti-aggregating action beneficial for these patients.
Immunosuppressants
Treatment of lupus based on this group of medicines is reserved for patients who do not respond adequately to treatment with antimalarials or glucocorticoids.
The most commonly used immunosuppressants to fight this disease are:
- Cyclophosphamide
- Mycophenolate mofetil
- Azathioprine
- Methotrexate
Biological therapies
These types of therapies are recent and are being studied through clinical trials. They are thus biological drugs, that is to say monoclonal antibodies, in particular belimumab and rituximab.
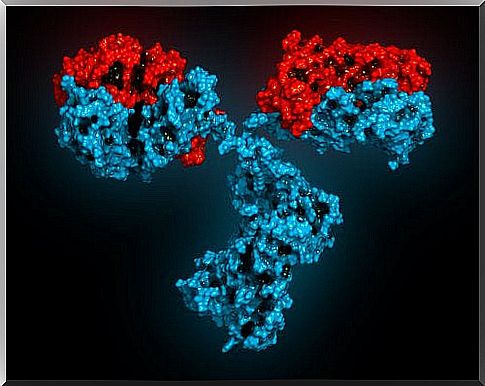
Belimumab is thus the first biologic drug approved as a specific treatment for SLE. But he is not the only one. This is because antimalarials are also an option, as we explained earlier.
The recommended dosage for belimumab is therefore 10 mg / kg on days 0, 14 and 28, then at 4 week intervals. If there is no improvement after 6 months of treatment, then the treatment should be stopped. Both drugs are currently under study.
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) also called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is indeed a rheumatic disease (a disease that affects the skin and connective tissue), considered to be the model for autoimmune diseases.