Everything You Need To Know About Pulmonary Embolism
Pulmonary embolism is a serious illness that can lead to the death of the patient. It is therefore important to lead a healthy lifestyle and not to have smoking habits.
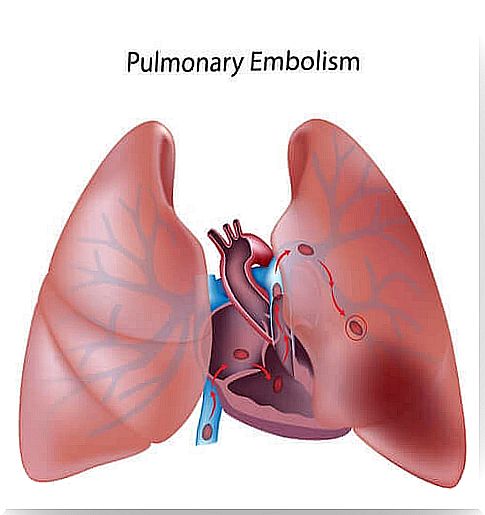
Pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening disease that occurs when parts of a thrombus break away from one place in the venous territory, migrate and become nailed in the pulmonary arteries.
In the majority of cases, embolisms come from a deep vein thrombosis of the extremities.
All of this results in a lack of oxygen in the lungs. It is one of the main medical emergencies. Moreover, its diagnosis is not easy because few signs can indicate to the doctor that the patient suffers from it.
The incidence of pulmonary embolism is estimated to be one in every 1,000 people per year, although it is likely that the figure is actually higher.
Causes of pulmonary embolism
In the majority of cases (about 95% of them), thrombus or coagulation forms in the veins of the lower limbs. It then migrates to the pulmonary artery.
It can also be air or fat. In the first case, we are dealing with an air embolism and, in the second, a fatty embolism. This occlusion mainly affects the lungs and the heart:
- One area of the lungs does not receive venous blood, which is low in oxygen and therefore will not be able to oxygenate it. This fact will have negative repercussions on the oxygen which will subsequently reach the rest of the organs and tissues of the patient.
- The heart will continue to pump blood to the lungs but, with the occlusion, it will face an obstacle. Pressure will build up in the pulmonary artery, weakening the heart’s right ventricle, which is the heart chamber that sends oxygen-free blood to the lungs.
Risk factors
There are several risk factors that favor the onset of pulmonary embolism. The most important are:
- Lower limb fractures or recent operations.
- Prolonged bed rest or immobilization.
- Long trips (over 8 hours).
- Hypercoagulable states.
- Cancer and treatment with chemotherapy.
- Obesity.
- Smoking.
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism

The clinical manifestations of pulmonary embolism are nonspecific. This is why it is difficult to make an early diagnosis. Some symptoms that might appear are:
- A feeling of suffocation. Small embolisms that do not cause symptoms can produce this sensation, if it does not occur because of a pulmonary infarction.
- Accelerated breathing which is accompanied by anxiety and restlessness.
- Sharp pain in the chest, especially when the person takes deep breaths.
- Dizziness and fainting or convulsions.
- Cyanosis or sudden death: these symptoms may appear if the patient has more than one large blocked pulmonary vessel.
- A cough, bloody sputum, and fever.
People with recurrent pulmonary embolism usually develop symptoms gradually, such as chronic choking, swelling of the ankles or legs, and weakness over weeks, months, or years.
Treatment
Treatment in the acute phase of pulmonary embolism aims to stabilize the patient, relieve symptoms, resolve vascular obstruction and prevent further episodes.
These goals are normally achieved with the administration of intravenous anticoagulant drugs. This treatment is administered for the first 5-10 days. The drug of choice for the treatment of pulmonary embolism is heparin.
In the most critical patients or who for some reason could not receive an anticoagulant drug, other treatments such as fibrinolysis may be requested to speed up the dissolution of the coagulation. You can also place a filter in the vena cava to prevent new thrombi from migrating to the lung.
Finally, once the patient has returned home, he will be prescribed oral anticoagulant medication. The most used and best known is the Sintrom. It is generally recommended to be administered for a minimum period of 3 months.
In patients who are at greater risk of pulmonary embolism, this quarterly period is usually prolonged and the drug ends up being given for life.