5 Facts To Know About Uterine Fibroids
Although uterine fibroids are not necessarily dangerous, it is advisable to undergo frequent gynecological examinations for early diagnosis, as well as treatment adequate.
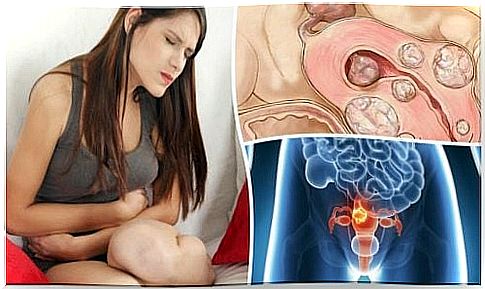
Uterine fibroids are abnormal growths of muscle tissue that form on the surface of the uterus and, more rarely, in the cervix.
Their presence is often alarming for women who have been diagnosed, but only 0.5% of them are caused by cancer cells. In other words, even if they cause gynecological discomfort, they very rarely represent a risk of cancer in this region.
Nonetheless, it is important to pay attention to uterine fibroids as they can interfere with reproductive and hormonal health. Therefore, we want to share 5 relevant data that every woman should know about the development of uterine fibroids.
1. What is a uterine fibroid?
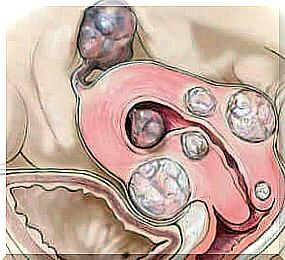
Uterine fibroids are a type of benign tumor that mostly occurs after 20 years.
Also called leiomyomas or fibromyomas, these are small masses of tissue, round in appearance, the size of which can be microscopic, but also large.
Their appearance is associated with genetic and hormonal factors. It is one of the causes of infertility in women.
2. What are the different types of uterine fibroids?
Fibroids are classified into four types, depending on their location in the matrix.
Submucosal fibroma
These are the ones that form just below the myometrium, in other words, the lining that protects the inner wall of the uterus. They can extend to the inner part of the uterine cavity, and when they enlarge, they can occupy a large part of it.
Subserous fibroma
These types of growths form just below the serosa. A layer that covers the outer part of the uterus. Their appearance gives the uterus a nodular appearance.
Pedicled fibroma
These fibroids are of the subserous type, but unlike the previous ones, they grow larger and eventually break away from the matrix. They are then suspended from a thin cord called a pedicle.
This type of tumor can grow inside or outside the uterine cavity.
Intramural fibroma
These are lumps that form inside the muscle wall of the uterus. When they get bigger, they can deform the outer and inner walls of the uterus.
3. What are the symptoms of uterine fibroids?

Although, in many cases, it is a difficult disease to detect due to the absence of symptoms, more than half of affected women experience changes that alert their presence.
We can therefore cite the following symptoms:
- Heavy and irregular menstrual bleeding.
- Inflammation and pain in the lower part of the stomach.
- Sudden increase in weight.
- Difficulty getting pregnant.
- High risk pregnancies and childbirth.
- Pain during coitus.
- Changes in urination habits.
- Lumbago.
4. How do uterine fibroids affect fertility?
One of the main concerns among women who are diagnosed with uterine fibroids is the impact on their reproductive health.
When tumors grow to a large size, they can actually affect fertility, or even complicate pregnancy.
The uterus itself increases in size due to the activity of estrogen. And since progesterone predominates during pregnancy, it is possible to carry out treatment to conceive a child.
However, it should be taken into account that the presence of uterine fibroids increases the risk of miscarriage during the first trimester of pregnancy.
5. What are the treatments for uterine fibroids?
Many women with uterine fibroids think that the only way to fight them is surgery. However, be aware that this is not the only treatment. Also, when they are too small, it is not necessary.
Usually, small growths are treated with pharmacological treatment. If they don’t respond to the effects and continue to grow, there is no choice but to extract them.
In this case, a myomectomy is performed which consists of removing the fibroids without affecting the uterus. In case of complications, a hysterectomy is performed, during which partial or total removal of the uterus is performed.
Attention to symptoms as well as regular pelvic examinations are critical to obtaining a timely diagnosis. Finally, although uterine fibroids are usually not serious, it is always advisable to consult a doctor to analyze the situation more deeply.