How To Detect Vision Problems In Children
It is important to carry out an ophthalmologic check from the age of four years, especially if in the family there is a history of eye disorder.
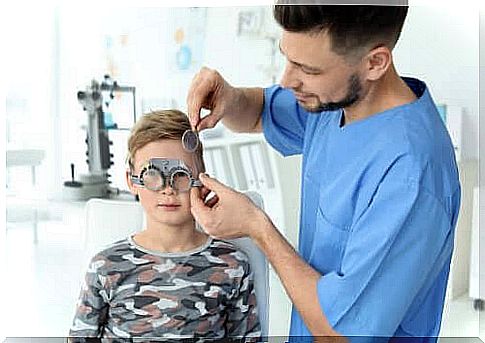
Some of the common vision problems in children such as strabismus or nearsightedness are relatively easy for parents to detect. However, there are other asymptomatic illnesses, which can then go unnoticed.
It is important to pay attention to a whole host of symptoms and warning signs that may indicate the presence of an eye disorder in the child :
- the child is not able to identify family members from afar
- he tends to bring objects closer to his eyes
- the child often rubs his eyes
- he tilts his head back to better observe something
- his vision is, at times, blurry
- the child has frequent headaches
The normal evolution of vision during the first year of life
During the child’s first year of life, the normal course of vision is as follows:
- 6 weeks: the child reacts to facial expressions
- 2-3 months: the child perceives movement and is able to follow a shiny object with his eyes
- 3-6 months: the child looks at his hand and is able to follow the activities of his environment
- 4 months: the child smiles while observing his own reflection in the mirror
- 6 months: the child perceives small objects and reaches them
- 7 months: the child touches his reflection in the mirror
- 9 months: the child bends down to see an object
- 1 year old: the child looks for toys and objects that he has lost sight of
To prevent a vision problem from becoming a chronic problem or an irreversible problem, it is important to carry out an ophthalmological check-up from the age of 4, especially if there is a family history of an eye disorder, whatever.
The most common vision problems in children are refractive errors such as nearsightedness, hyperopia, and stigmatism. Strabismus, amblyopia, and dyschromatopsia (changes in color) are other common problems.
The most common vision problems in children

Amblyopia
Amblyopia affects between 2-5% of the population and is one of the most common causes of vision loss in developed countries. Early diagnosis and treatment is the key to preventing disease progression into adulthood.
Special attention should be paid to the child’s vision if it was born prematurely and if there is a history of amblyopia in the family or refractive errors or retinal problems .
Although this disorder is usually asymptomatic, certain discomforts such as headaches or neck pain may indicate the presence of this disorder. Also, once the child can read, it is possible that he skips words or confuses certain letters.
Strabismus
Strabismus affects between 3 and 6% of the population. It is important to diagnose this disorder in time because it is possible to correct this disorder in children with the help of treatment. In adulthood, this is no longer possible.
The most common symptoms of strabismus are:
- poor eye alignment
- the eyes do not move in the same direction
- tilting the head to one side to look at concrete points
- the child blinks or rubs their eyes often
- the child narrows his eyes to see better
Refractive errors, common vision problems in children

Refraction problems such as astigmatism, myopia or even hyperopia affect about 20% of children.
Myopia
Myopia appears around the age of six.
Opening your eyes to observe something in the distance and confusing people who are at a more or less distant distance are two warning signs of myopia. Some children bring objects closer to their eyes or squint their eyes to see better.
Hyperopia
Hyperopia is usually physiological, which is why it affects most infants. It disappears as the eyes grow.
However, in some cases, this disorder persists for life. If hyperopia is strong and has not been corrected, it can cause amblyopia or strabismus.
Headaches during an activity that intensely involves vision and eye fatigue after this type of activity are other annoyances associated with hyperopia.
Astigmatism
When the light emanating from objects enters the eye and focuses on different points of the retina, then there is astigmatism.
Astigmatism is an abnormality characterized by blurry and distorted vision. This concerns both near objects and those which are far away.
Did you know the warning signs for vision problems in children? If you notice these symptoms in your child, see a trusted specialist as soon as possible.
Only an eye health specialist will be able to determine the type of problem your child has and prescribe the correct treatment.