Salicylic Acid, What Is It?
Salicylic acid belongs to the group of analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory agents. It was first described during the 18th century by Richard Stone. This reverend found that infusions of the bark of the white willow tree helped cure fever.

Salicylic acid is a substance that has keratolytic and antimicrobial properties. This acid is used for example in dermatology. Indeed, it is able to promote the desquamation of the skin in order to avoid contamination by bacteria or opportunistic fungi.
In addition, this acid is able to regulate the viscosity of the skin and also acts as an anti-inflammatory. For these reasons, this substance is considered essential for improving the appearance of aged skin.
Where does salicylic acid come from?
The bark of the white willow, Salix alba , contains salicin, and this is where salicylic acid is extracted. However, this alpha hydroxy acid can be found in other plants such as wintergreen or birch.
Salicylic acid belongs to the group of analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory agents. It was first described in the 18th century by Richard Stone. This reverend found that infusions of the bark of the white willow tree helped cure fever.
During the year 1899, this substance was synthesized for the first time to replace quinine when it came to controlling fever and oral pain. Salicylic acid was one of its metabolites and could be applied topically.
The actions and effects of salicylic acid
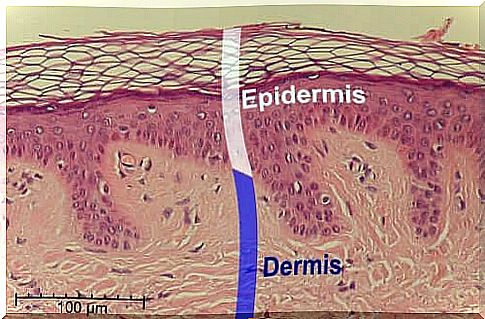
This acid has an impact on the structure of the skin. Salicylic acid affects the cohesion between queratinocites, a type of cells, and their desquamation.
As we mentioned above, this acid acts as a keratolytic and an antimicrobial in concentrations of 5-10%. In addition, it has a direct anti-inflammatory effect, although this has not yet been confirmed. In lower concentrations, 1 to 3%, it acts as a keratoplastic.
Keratoplastic substances promote regeneration of the stratum corneum and normalize defective keratinization. As for keratolitics, these are able to cause the fall of the cornea or reduce its thickness.
In addition, it is important to emphasize that salicylic acid is a fat soluble substance, that is to say that it can be mixed and diluted in the fats of the epidermis and in the sebaceous material which is stuck in the follicles. When salicylic acid enters the lipidic areas of the skin, it causes exfoliation and flaking of the skin .
Indications
There are nine essential indications for salicylic acid:
- Keratolytic: in the concentrations mentioned, this acid is used to treat common, flat or plantar warts
- Keratoplastic: 0.5% at the edge of dull ulcers
- Skin problems: it can be used alone in concentrations of 10 to 15% as a cream or ointment, or with alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or retinoic acid
- Photoprotection: it acts as a chemical filter
- Antifungal: It promotes the penetration of topical antifungal drugs by removing the stratum corneum
- Anesthetic: salicylic acid has a certain anesthetic effect because it is involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins, substances related to pain. This acid is, for example, used to relieve the pain of canker sores
- Pain reliever: certain derivatives of salicylic acid are used to relieve pain associated with bursitis as well as muscle pain
- Antipruritics: salicylic acid relieves itching
- Anti-inflammatory: as is the case for its analgesic effect and its anesthetic effect, its anti-inflammatory effect derives from its ability to inhibit the synthesis of protaglandins
Adverse effects of salicylic acid
As with all medicines and chemicals, salicylic acid also has side effects.
Below are its most common side effects:
- Systemic absorption toxicity: when the substance is in the blood it can cause nausea and vomiting
- Antifungal and teratogenic effect: this acid can affect cell division and affect the fetus. This acid is therefore contraindicated for pregnant women
- Allergic reactions: this acid is contraindicated in people who are allergic to this substance, as it can cause serious complications.
- Mental disorders: this side effect is less common compared to the other side effects listed above
In short, salicylic acid is still relevant today with regard to its traditional indications as well as other more recent indications. It is an effective and reliable substance.