What Are The Causes Of Dry Skin?
Dry skin is a very common condition among the population. Aging, exposure to cold or to the action of external irritants are responsible for skin dryness. Find out more in this article.

Dry skin or xerosis is a common skin condition that affects people of different ages and in different areas of the body. The skin requires a water content of 10 to 15% to remain supple and intact. Lower values therefore affect its turgor. What are the causes of dry skin?
When the skin is dry, it causes itching which then leads to an excoriation and risk of infection. This effect can be minimized by increasing environmental humidity, modifying hygiene products and using emollients to replace lipid components.
What are the manifestations of dry skin?
Too dry skin loses a lot of moisture and becomes dehydrated considerably. According to the American Academy of Dermatology , the signs and symptoms are as follows:
- Dryness with more pronounced fine lines.
- Itching or pruritus.
- Fine peeling.
- Roughness to the touch.
- Redness.
Dry skin can affect any part of the body, most commonly the hands, arms and legs. The objectives of dermatological hydration are therefore to improve its appearance and function since it is a large organ that fulfills multiple roles within the human body.

What are the causes of dry skin?
The xerosis is a common condition experienced by millions of people. It can appear chronically or acutely in response to environmental changes, skin care, or illness.
Most humans experience the signs of dry skin at some point. This can be attributed to both exogenous and endogenous factors. Here are the most frequent and best known.
Diseases
Diabetes, diseases of the thyroid gland and kidneys, contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis, are conditions that lead to excessively dry skin. They affect the moisture content of the stratum corneum and dermis in different ways.
The main symptom that testifies to this manifestation is itching. In other words, the permanent itch resulting from drought. It is therefore fundamental to maintain the skin barrier with emollients in patients suffering from these pathologies.
Extreme climates, one of the causes of dry skin
Living in colder climates, especially during the winter months, when the outside air is dry as is the heating, causes blood to be forced out of the dermis. Or in hot, dry climates, where heat and air conditioning evaporate water from the skin. These are all predisposing factors.
In this context, it is better to reduce the time for showering and washing with lukewarm water. Then, it is strongly recommended to apply an emollient.
Excessive baths
Excessive and frequent bathing also dries out the skin. Many products contain surfactants which extract and emulsify lipids from the skin surface as well as intracellular ones. This then damages the skin barrier in the medium term.
Furthermore, exposure to harsh chemicals also destroys the skin barrier. The protective lipid layer is lost and external aggressions penetrate more deeply.
Aging
The prevalence of xerosis increases with age. This is due to changes in the keratinization process and the lipid content of the stratum corneum.
The elderly are therefore more likely to develop dry skin. With age, the dermis produces less sebum, which is responsible for the softness and youthfulness of the skin. This dries up the surfaces and prevents proper protection against irritants.
At the age of 40, the amount of sebum produced by the body drops dramatically. Then, after 40 years, the amount of sebum continues to decrease, which increases the risk of dry skin. Although it is already common, xerosis is a condition that will become more and more common as the population ages.
Smoking, one of the causes of dry skin
Cigarettes contain harmful chemicals that speed up the rate of aging of the skin, making it drier.
On the other hand, smokers have dry, gray facial skin with the typical wrinkles around the mouth. Smoking actually increases the breakdown of collagen and elastic fibers that form the basic structure of the dermis. This then accelerates the aging process.
What is skin pH and how does it affect dry skin?
The top layer of human skin is characterized by a pH of 4-6. This figure indicates the degree of acidity of substances. It also indicates a slight acidification of the cell layer, due to amino acids, fatty acids and sebum.
All of these components are acids and, when present together on human skin, they become a barrier that prevents the colonization of bacteria. Likewise, the lipid barrier, which is made up of free fatty acids, cholesterol and ceramides, functions as a water repellant.
Most human pathogenic bacteria are inhibited by the acidic pH of the surface of normal skin. However, this shield is altered when the skin is injured or dry.
The subcutaneous tissue has a physiological pH of 7.4. This promotes bacterial colonization in case the barriers do not work. This is what these studies carried out by the International Journal of Cosmetic Science underline . Therefore, xerosis becomes a risk factor for infectious dermatitis.
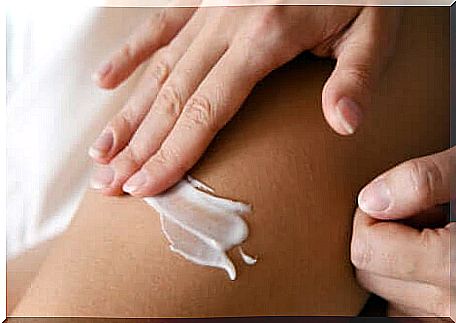
Moisturize dry skin
The ideal for dry skin or xerosis is to take small showers with lukewarm water and then apply a moisturizer. This is when the skin is more receptive to absorb it and maintain its skin barrier.
Finally, itching is a classic symptom. Thus, in the event of recurrent itching, it should be interpreted as dehydrated skin and provide it with sufficient hydration.